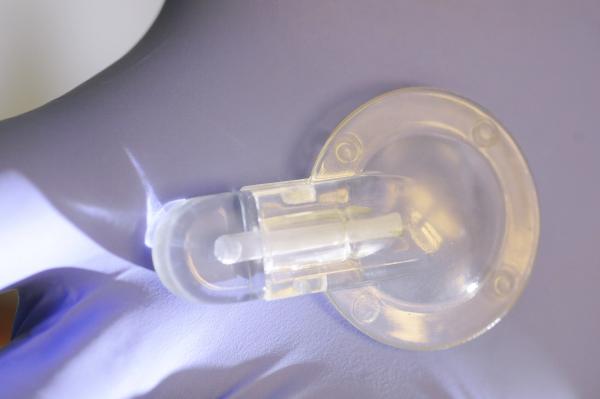
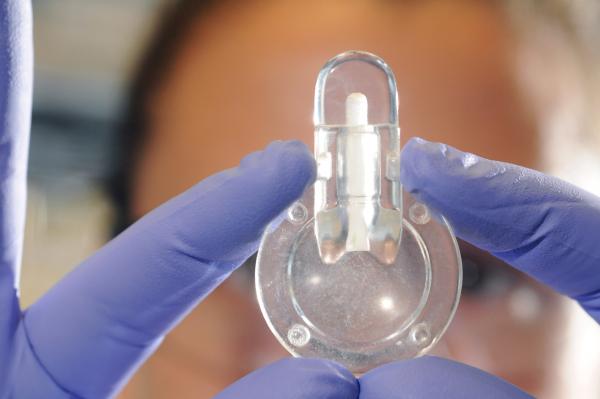
A simple point-of-care testing device for anemia could provide more rapid diagnosis of the common blood disorder and allow inexpensive at-home self-monitoring of persons with chronic forms of the disease.
The disposable self-testing device analyzes a single droplet of blood using a chemical reagent that produces visible color changes corresponding to different levels of anemia. The basic test produces results in about 60 seconds and requires no electrical power. A companion smartphone application can automatically correlate the visual results to specific blood hemoglobin levels.
By allowing rapid diagnosis and more convenient monitoring of patients with chronic anemia, the device could help patients receive treatment before the disease becomes severe, potentially heading off emergency room visits and hospitalizations. Anemia, which affects two billion people worldwide, is now diagnosed and monitored using blood tests done with costly test equipment maintained in hospitals, clinics or commercial laboratories.
Because of its simplicity and ability to deliver results without electricity, the device could also be used in resource-poor nations.
A paper describing the device and comparing its sensitivity to gold-standard anemia testing was published August 30, 2014, in The Journal of Clinical Investigation. Development of the test has been supported by the FDA-funded Atlantic Pediatric Device Consortium, the Georgia Research Alliance, Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, the Georgia Center of Innovation for Manufacturing and the Global Center for Medical Innovation.
“Our goal is to get this device into patients’ hands so they can diagnose and monitor anemia themselves,” said Dr. Wilbur Lam, senior author of the paper and a physician in the Aflac Cancer and Blood Disorders Center at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and the Department of Pediatrics at the Emory University School of Medicine. “Patients could use this device in a way that’s very similar to how diabetics use glucose-monitoring devices, but this will be even simpler because this is a visual-based test that doesn’t require an additional electrical device to analyze the results.”
The test device was developed in a collaboration of Emory University, Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and the Georgia Institute of Technology – all based in Atlanta. It grew out of a 2011 undergraduate senior design project in the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering at Georgia Tech and Emory University. In 2013, it was among the winners of Georgia Tech’s InVenture Prize, an innovation competition for undergraduate students, and won first place in the Ideas to SERVE Competition in Georgia Tech’s Scheller College of Business.
Using a two-piece prototype device, the test works this way: A patient sticks a finger with a lance similar to those used by diabetics to produce a droplet of blood. The device’s cap, a small vial, is then touched to the droplet, drawing in a precise amount of blood using capillary action. The cap containing the blood sample is then placed onto the body of the clear plastic test kit, which contains the chemical reagent. After the cap is closed, the device is briefly shaken to mix the blood and reagent.
“When the capillary is filled, we have a very precise volume of blood, about five microliters, which is less than a droplet – much less than what is required by other anemia tests,” explained Erika Tyburski, the paper’s first author and leader of the undergraduate team that developed the device.
Blood hemoglobin then serves as a catalyst for a reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction that takes place in the device. After about 45 seconds, the reaction is complete and the patient sees a color ranging from green-blue to red, indicating the degree of anemia.
The colors are produced by a redox-sensitive dye that complements the color arising from the hemoglobin, explained L. Andrew Lyon, who supported the work while he was chair of Georgia Tech’s School of Chemistry & Biochemistry. “It is the breadth of color space covered by the reaction that really enables the assay to be so reliable when read out by the naked eye,” said Lyon, who is now dean of the Schmid College of Science and Technology at Chapman University in California.
A label on the device helps with interpretation of the color, or the device could be photographed with a smartphone running an application written by Georgia Tech undergraduate student Alex Weiss and graduate student William Stoy. The app automatically correlates the color to a specific hemoglobin level, and could one day be used to report the data to a physician.
To evaluate sensitivity and specificity of the device, Tyburski studied blood taken from 238 patients, some of them children at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and the others adults at Emory University’s Winship Cancer Institute. Each blood sample was tested four times using the device, and the results were compared to reports provided by conventional hematology analyzers.
The work showed that the results of the one-minute test were consistent with those of the conventional analysis. The smartphone app produced the best results for measuring severe anemia.
“The test doesn’t require a skilled technician or a draw of venous blood and you see the results immediately,” said Lam, who is also an assistant professor in the Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering. “We think this is an empowering system, both for the general public and for our patients.”
Tyburski and Lam have teamed up with two other partners and worked with Emory’s Office of Technology Transfer to launch a startup company, Sanguina, to commercialize the test, which will be known as AnemoCheck™. The test ultimately will require approval from the FDA. The team also plans to study how the test may be applied to specific diseases, such as sickle cell anemia – which is common in Georgia.
The device could be on pharmacy shelves sometime in 2016, where it might help people like Tyburski, who has suffered mild anemia most of her life. “If I’d had this when I was kid, I could have avoided some trips to the emergency room when I passed out in gym class,” she said.
About a third of the population is at risk for anemia, which can cause neurocognitive deficits in children, organ failure and less serious effects such as chronic fatigue. Women, children, the elderly and those with chronic conditions such as kidney disease are more likely to suffer from anemia.
Research News
Georgia Institute of Technology
177 North Avenue
Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0181 USA
Media Relations Assistance: Georgia Tech -- John Toon (jtoon@gatech.edu) (404-894-6986) or Brett Israel (brett.israel@comm.gatech.edu) (404-385-1933) or Emory University -- Holly Korschun (hkorsch@emory.edu) (404-727-3990).
Writer: John Toon
Media Contact
John Toon
Research News
(404) 894-6986
Latest BME News
Jo honored for his impact on science and mentorship
The department rises to the top in biomedical engineering programs for undergraduate education.
Commercialization program in Coulter BME announces project teams who will receive support to get their research to market.
Courses in the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering are being reformatted to incorporate AI and machine learning so students are prepared for a data-driven biotech sector.
Influenced by her mother's journey in engineering, Sriya Surapaneni hopes to inspire other young women in the field.
Coulter BME Professor Earns Tenure, Eyes Future of Innovation in Health and Medicine
The grant will fund the development of cutting-edge technology that could detect colorectal cancer through a simple breath test
The surgical support device landed Coulter BME its 4th consecutive win for the College of Engineering competition.