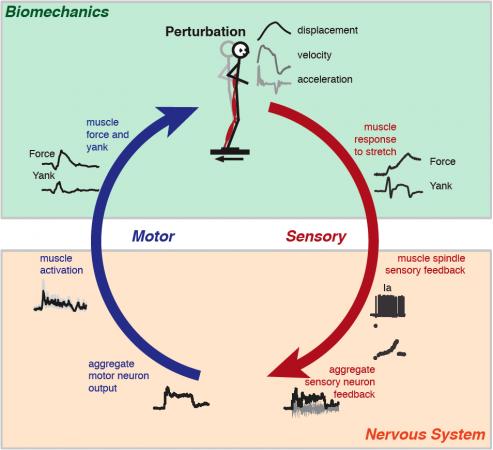
Biologists and biomedical engineers are proposing to define the term “yank” for changes in force over time, something that muscles cause and nerves can feel and respond to.
Their ideas were published on September 12 in Journal of Experimental Biology.
Expressed mathematically, acceleration is the derivative of speed or velocity with respect to time. The term for the time derivative of acceleration is “jerk,” and additional time derivatives after jerk are called “snap,” “crackle” and “pop.”
The corresponding term for force – in physics, force is measured in units of mass times acceleration – has never been defined, the researchers say.
Scientists that study sports often use the term “rate of force development”, a measure of explosive strength. Scientists who study gait and balance -- in animals and humans -- also often analyze how quickly forces on the body change. It could be useful in understanding spasticity, the abnormal activation of muscles from reflexes seen in multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, stroke and cerebral palsy.
“Understanding how reflexes and sensory signals from the muscles are affected by neurological disorders is how we ended up needing to define the rate change in force,” says Lena Ting, a researcher in the Petit Institute for Bioengineering and Bioscience and professor of rehabilitation medicine in the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering at Georgia Tech and Emory.
Her co-authors are David Lin (Washington State University), Craig McGowan (University of Idaho), and Kyle Blum, a postdoctoral fellow at Northwestern who previously worked with Ting.
Ting says Lin originally introduced her and Blum to the term “yank”.
“Dr. Ting and I were thinking similarly – but separately – that current terminology describing the time derivative of force was too unwieldy and limiting,” Lin says. “During an American Society of Biomechanics meeting, I suggested that ‘yank’ was a possible term that we could use.”
On a large scale, yank is relevant to the study of jumping, sprinting, capturing prey and maintaining balance, the researchers say. It is similarly useful in analyzing the behavior of muscles and tendons, sensory feedback and spinal reflexes, all the way down to the contributions of individual cells.
A companion paper from Blum and Ting shows that in the leg muscles of a rat, yank in muscle fibers corresponds to the firing rates of muscle spindles, which are stretch receptors that detect changes in length of the muscle. Muscle spindles send signals to the nervous system so that the animal is aware of the body’s position in space. (see graph)
The authors’ research is supported by the Army Research Office (ARO 66554-EG), the National Science Foundation (NSF 1553550) and the National Institutes of Health (R01HD90642, R01HD46922, F31NS093855).
Media Contact
Keywords
Latest BME News
Jo honored for his impact on science and mentorship
The department rises to the top in biomedical engineering programs for undergraduate education.
Commercialization program in Coulter BME announces project teams who will receive support to get their research to market.
Courses in the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering are being reformatted to incorporate AI and machine learning so students are prepared for a data-driven biotech sector.
Influenced by her mother's journey in engineering, Sriya Surapaneni hopes to inspire other young women in the field.
Coulter BME Professor Earns Tenure, Eyes Future of Innovation in Health and Medicine
The grant will fund the development of cutting-edge technology that could detect colorectal cancer through a simple breath test
The surgical support device landed Coulter BME its 4th consecutive win for the College of Engineering competition.